Difference between revisions of "Greater Rhea"
Mistiryshak (talk | contribs) m |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
{{FriendBuilder | {{FriendBuilder | ||
|introduction='''Greater Rhea''' is a type of [[Friend]] that appeared in the original Kemono Friends mobile game. | |introduction='''Greater Rhea''' is a type of [[Friend]] that appeared in the original Kemono Friends mobile game. | ||
| + | |appearance=Greater Rhea has orange eyes and short white hair, it fades to black on her middlemost bang to resemble a beak, and a portion of hair on the upper side of her head is gray in color and has a cowlick at the top. She wears a golden circlet with a red jewel, while she also has the characteristics of a Bird Friend, such as the pair of wings and the very big animal tail, both being gray tipped in white, and ending in a black color. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Greater Rhea wears a white ripped bare midriff shirt with a sailor collar and a pink ribbon tie, a long scarf that is black in the middle and changes to white on the sides, and a pair of black arm sleeves with golden decorations on the ends. On her lower body she wears a long skirt that is white on top, black on the middle and then ends with a pink fur, all being held by a black belt with a gold buckle. White leggings and a pair of black Mary Jane shoes complement her attire. | ||
| + | |reallife=[[File:greater_rhea.jpg|thumb|upright=1.0|left]]The greater Rhea is a large flightless bird native to south america. It's the largest bird species of the Americas. Their plumage is grey with some black and a black ring around their neck. The feathers are long and plume-like, since they aren't used for flying. Their feet are long and powerful legs are grey and developed for running. Usually their diet consists of plants, seeds and fruits but they also often eat lizards, small birds and insects. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Male greater rhea will become territorial and solitary during the breeding season in spring. They build big nests and try to attract female mates by dancing and calling. The females will each lay an egg into one males nest every other day for a few days until they move to the next nest. The eggs will hatch after about 35-40 days and they will follow the male, who will take care of them for around 6 months. The males will be very territorial and protective of their young during that time. The young are ready for breeding with 2 years of age for females and 3 years for males. | ||
| + | |||
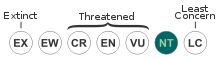
| + | During winter, the greater rhea lives in groups of around 30 birds who will graze along other herds of animals, like deer and domestic animals, in order to look for more food and protection from predators. Both the greater rhea and its eggs are used for food, its skin as leather and feathers for feather dusters. The bird is seen as a pest for farmers even though they benefit farming by eating insects and weeds from the crops. Though they like crops, habitat loss for farmland is a major issue for the greater rhea populations in south america; overall, the bird is still classified as near threatened. | ||
| + | |trivia=*In 2000, a group of 7 greater rheas, consisting of 3 males and 4 females, escaped a private enclosure near Lübeck, Germany. Due to the sparsely populated area which was difficult to access, the birds managed to escape officials long enough for them to give up, expecting the rheas to be unable to survive the German climate and die off. However, the birds seem to thrive in the area, current population estimates are at 220 specimen living in a 150qm area east of the Ratzeburger See in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. conservationists are concerned about the invasiveness and impact of the greater rhea on native fauna, flora and crops but evidence suggests there is next to no negative impact. The species is still on the "grey list", meaning they will be observed for their invasive potential. By law, the bird has acquired the status of native species (by surviving for 3 generations without human help) in Germany and qualifies for special protection. | ||
| + | |reference=*http://www.woburnsafari.co.uk/discover/meet-the-animals/birds/greater-rhea/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | *http://www.10000birds.com/greater-rheas-germanys-new-big-bird.htm | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | {{BirdFriendsNav}} | |
| − | [[Category:Real Animal Friends]] [[Category: | + | [[Category:Real Animal Friends]] [[Category:Bird Friends]] [[Category:Ratite Friends]] [[Category:Nexon Game Debuts]] |
Revision as of 18:12, 6 March 2018
| Greater Rhea | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Character Data | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| Animal Data | ||||||||||||
|
| Greater Rhea | Festival | Pavilion | KF3 | Nexon Game | Gallery |
Greater Rhea is a type of Friend that appeared in the original Kemono Friends mobile game.
Appearance
Greater Rhea has orange eyes and short white hair, it fades to black on her middlemost bang to resemble a beak, and a portion of hair on the upper side of her head is gray in color and has a cowlick at the top. She wears a golden circlet with a red jewel, while she also has the characteristics of a Bird Friend, such as the pair of wings and the very big animal tail, both being gray tipped in white, and ending in a black color.
Greater Rhea wears a white ripped bare midriff shirt with a sailor collar and a pink ribbon tie, a long scarf that is black in the middle and changes to white on the sides, and a pair of black arm sleeves with golden decorations on the ends. On her lower body she wears a long skirt that is white on top, black on the middle and then ends with a pink fur, all being held by a black belt with a gold buckle. White leggings and a pair of black Mary Jane shoes complement her attire.
Series Appearances
| Media | Role | |
|---|---|---|
In Real Life
The greater Rhea is a large flightless bird native to south america. It's the largest bird species of the Americas. Their plumage is grey with some black and a black ring around their neck. The feathers are long and plume-like, since they aren't used for flying. Their feet are long and powerful legs are grey and developed for running. Usually their diet consists of plants, seeds and fruits but they also often eat lizards, small birds and insects.
Male greater rhea will become territorial and solitary during the breeding season in spring. They build big nests and try to attract female mates by dancing and calling. The females will each lay an egg into one males nest every other day for a few days until they move to the next nest. The eggs will hatch after about 35-40 days and they will follow the male, who will take care of them for around 6 months. The males will be very territorial and protective of their young during that time. The young are ready for breeding with 2 years of age for females and 3 years for males.
During winter, the greater rhea lives in groups of around 30 birds who will graze along other herds of animals, like deer and domestic animals, in order to look for more food and protection from predators. Both the greater rhea and its eggs are used for food, its skin as leather and feathers for feather dusters. The bird is seen as a pest for farmers even though they benefit farming by eating insects and weeds from the crops. Though they like crops, habitat loss for farmland is a major issue for the greater rhea populations in south america; overall, the bird is still classified as near threatened.
Trivia
- In 2000, a group of 7 greater rheas, consisting of 3 males and 4 females, escaped a private enclosure near Lübeck, Germany. Due to the sparsely populated area which was difficult to access, the birds managed to escape officials long enough for them to give up, expecting the rheas to be unable to survive the German climate and die off. However, the birds seem to thrive in the area, current population estimates are at 220 specimen living in a 150qm area east of the Ratzeburger See in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. conservationists are concerned about the invasiveness and impact of the greater rhea on native fauna, flora and crops but evidence suggests there is next to no negative impact. The species is still on the "grey list", meaning they will be observed for their invasive potential. By law, the bird has acquired the status of native species (by surviving for 3 generations without human help) in Germany and qualifies for special protection.